PubMed Full-Text Access
The Eccles Health Sciences Library at the University of Utah is spearheading an initiative to enable Utah-licensed physicians to retrieve full-text articles from PubMed without encountering a publisher paywall. Read on to learn more about this pilot program, how it can benefit you, and how you can participate.
Background
Medical knowledge has increased exponentially over the past several decades and has reached a point where it doubles in volume every 73 days[i]. This body of growing evidence is primarily disseminated via publication in medical journals, at an estimated rate of 3 million articles per year being published in over 35,000 biomedical journals. PubMed, which searches the MEDLINE database of biomedical literature, ingests approximately 1 million new papers each year[ii]. Despite the massive volume of clinically relevant information that is generated and published, approximately 75% of it remains behind publisher paywalls and therefore inaccessible to individuals without costly personal or institutional subscriptions to the content[iii].
Paywalls Inhibit Evidence-Based Practice
Research confirms that patient outcomes improve when healthcare providers practice in an evidence-based manner[iv]. Evidence-based practice (EBP) is “the conscientious, explicit, and judicious use of current best evidence in making decisions about the care of the individual patient. It means integrating individual clinical expertise with the best available external clinical evidence from systematic research”[v]. In order to use the best available external evidence, physicians must be able to access and appraise current relevant research. EBP’s mandate of incorporating the best available evidence is rendered nearly impossible when that research is withheld from healthcare providers due to paywall restrictions. Lack of access to the corpus of evidence undermines providers’ ability to engage in evidence-based practice and withholds EBP’s potential benefits from their patients.
Expanding Access to the Evidence – a Pilot Program
Through the creation of a special PubMed interface, powered by an article delivery service, the Eccles Library has devised a pathway for Utah physicians to retrieve full-text articles – even without having a subscription to the journal. The goal is to allow physicians unfettered access to the evidence – and determine if this particular method of doing so is sustainable and, potentially, scalable.
PubMed Full-text Access: How it Works
Register for an Account (watch 1 min video demo)
Step 1
Interested physicians are invited to submit a registration request
Step 2
After receiving your request and verifying your status as a currently licensed Utah physician, Eccles Library personnel will create an account for you using Article Galaxy’s Reprints Desk article delivery service.
Step 3
Once your account is established, you will receive a welcome email from Reprints Desk containing your login credentials. Note: You will need to reset the password prior to using your account.
Find Articles (watch 1 min video demo)
Step 1
Search this customized PubMed interface enabled with Reprints Desk functionality
Step 2
After finding an article of interest, click on the linked title of the article. Look for and select the “Get Full-Text in Article Galaxy” icon:

Step 3
Clicking the “Get Full-Text in Article Galaxy” will launch a screen where you can enter the credentials you created:
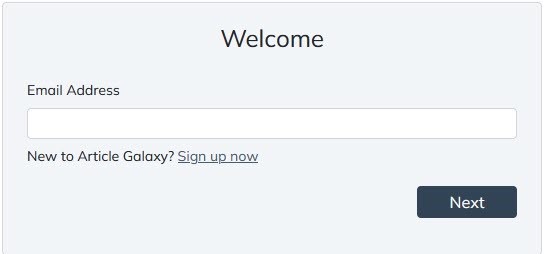
Step 4
After you sign in, you’ll see an order form – auto-populated with the PubMed article information:
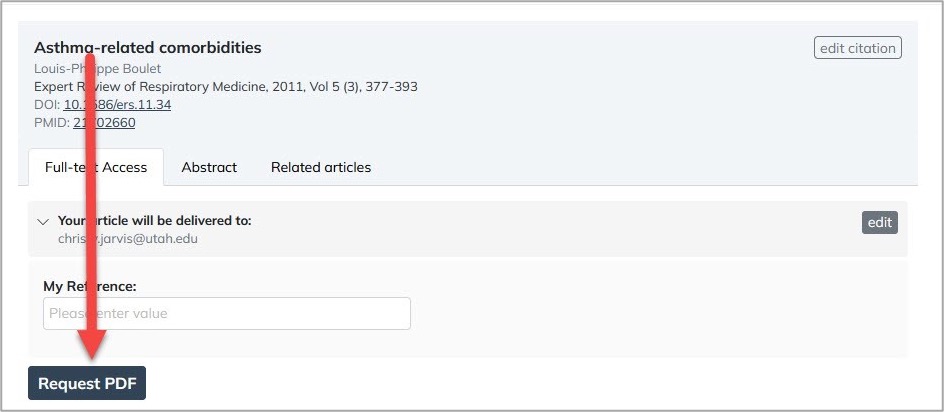
Step 5
Click Request PDF. If the article is immediately available, it will load in your browser; otherwise, it will be sent to your registered email address.
Frequently Asked Questions
Who can use this service?
All actively licensed physicians in Utah are eligible to register for, and use, this service. Your license number will be verified prior to activating your account.
What about other providers?
For now, this service is limited to M.D. and D.O. providers across the state. Eccles Library will evaluate usage and cost data throughout the pilot program to determine sustainability and scalability to potentially include additional categories of providers, such as P.A.s and N.P.s
Are there any limitations?
While the service is new and undergoing evaluation, the following limits are in place:
- This service is limited to a cost of $100 per article. Requests that exceed $100 will not be filled.
- There is a limit of 150 articles per calendar year, per registered user.
Where can I get more information?
Additional info is available online at: https://campusguides.lib.utah.edu/utahproviders . You can also contact the Eccles Library with questions or to get help.
[i] Densen P. Challenges and opportunities facing medical education. Transactions of the American Clinical and
Climatological Association. 2011;122:48. PMC3116346
[ii] White K. Publications Output: US Trends and International Comparisons. Science & Engineering Indicators 2020.
NSB-2020-6. National Science Foundation. 2019
[iii] Piwowar H, Priem J, Larivière V, Alperin JP, Matthias L, Norlander B, et al. The state of OA: a large-scale analysis
of the prevalence and impact of Open Access articles. PeerJ. 2018;6:e4375. PMC5815332
[iv] Fineout-Overholt E, Melnyk BM, Schultz A. Transforming health care from the inside out: advancing evidence based
practice in the 21st century. Journal of professional nursing. 2005;21(6):335-44.
[v] Sackett DL, Rosenberg WM, Gray JM, Haynes RB, Richardson WS. Evidence based medicine: what it is and what
it isn’t. BMJ.1996;312(7023):71-2. PMC2349778.










