| Schedule | Lectures | Seminars | Tests | Glossary | Cases | Index | Review | Search | Feedback | |
| Schedule | Lectures | Seminars | Tests | Glossary | Cases | Index | Review | Search | Feedback | |
Follicular cysts or corpus luteum cysts are often referred to as functional cysts of the ovary. An asymptomatic simple unilocular cyst visualized by ultrasound may be followed for a 2-6 weeks to determine whether it will resolve spontaneously. :
 Click here for a larger view |
Benign cyst.
Here is a benign cyst in an ovary. This is probably a follicular cyst.
Occasionally such cysts may reach several centimeters in size and, if they
rupture, can cause abdominal pain.
Credits: C. Matthew Peterson, M.D. |
Many physicians choose to suppress gonadotropins with oral contraceptives. The oral contraceptives suppress gonadotropins which support "functional cysts" .
Physiologically normal ovarian enlargement can be due to the development or persistence of follicular or corpus luteum cysts. Follicular cysts are usually thin walled, 2-6 cm in diameter and contain relatively clear fluid. Most regress spontaneously in 1-3 months. Occasionally they can enlarge significantly and may result in bleeding from a rupture in the cyst wall. Large functional cysts and ovarian neoplasms may result in torsion.
 Click here for a larger view |
Mature cystic teratoma-torsed with adenexal structures.
Elements of all three germ layers are present:
endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm. They are
classified as germ cell tumors and are thought to
arise through parthenogenesis. They are found in
the path of migration of the germ cells from the
yolk sac to the primitive gonad.
Credits: Alan B.P. Ng |
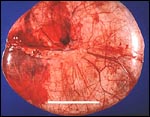 Click here for a larger view |
Serous cystadenoma.
These tumors comprise 20% of all ovarian neoplasms.
The epithelium is a single layer of regular
cuboidal epithelium, with basal nuclei and rare
mitoses.
Credits: Alan B.P. Ng |
When ovaries torse on their suspensory ligament they nearly always rotate medially. The epithelial lining of the follicular cyst has low cuboidid cells.
 Click here for a larger view |
Epithelium of a follicular cyst.
Low cuboidal cells are found in the lining of
follicular cysts.
Credits: Alan B.P. Ng |
Corpus luteum cysts exhibit a convoluted lining with luteinized granulosa and theca cells.