| Schedule | Lectures | Seminars | Tests | Glossary | Cases | Index | Review | Search | Feedback | |
| Schedule | Lectures | Seminars | Tests | Glossary | Cases | Index | Review | Search | Feedback | |
Other causes of ovarian enlargement include polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS), theca lutein, and granulosa and or theca cell tumors. Polycystic ovarian syndrome is a spectrum of related disorders which numerically is the most common cause of bilateral ovarian enlargement. This disorder is characterized by anovulation or oligoovulation, hyperandrogenemia, and often obesity.
 Click here for a larger view |
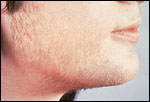
Hirsutism.
This woman has polycystic ovarian syndrome and hyperandrogenemia resulting in hirsutism.
Credits: C. Matthew Peterson,M.D. |
Increased luteinizing hormone levels (LH) are often detected. Approximately, 3-7% of the female population have this syndrome. The ovaries of affected patients have a thickened, white cortex with numerous small follicular cysts surrounding the periphery which usually measure 10 mm or less.
 Click here for a larger view |
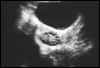
Polycystic ovary-pearl necklace sign.
Underlying the bladder is the ovary with a
classical polycystic appearance often referred
to as a "pearl necklace".
Credits: Paula Woodward, M.D. |
Conditions with high levels of human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG) such as gestational trophoblastic neoplasia, choriocarcinoma, and occasionally in a normal pregnancy can be associated with the development of multiple theca lutein cysts.
 Click here for a larger view |
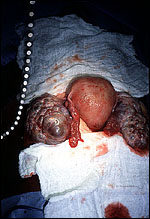
Theca lutein cysts.
Normal pregnancies, gestational trophoblastic
neoplasia, and choriocarcinoma may be associated
with theca lutein cysts.
Credits: C. Matthew Peterson, M.D. |
Microscopically the ovaries have multiple theca lutein cysts which have prominent luteinization of the thecal compartment.
 Click here for a larger view |
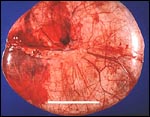
Serous cystadenomas.
These tumors comprise 20% of all ovarian neoplasms.
The epithelium is a single layer of regular
cuboidal epithelium, with basal nuclei and rare
mitoses.
Credits: Alan B.P. Ng |
Stromal edema and luteinization may also be seen. When this condition exists in association with gestational trophoblastic neoplasia it is termed hyperreaction luteinalis.